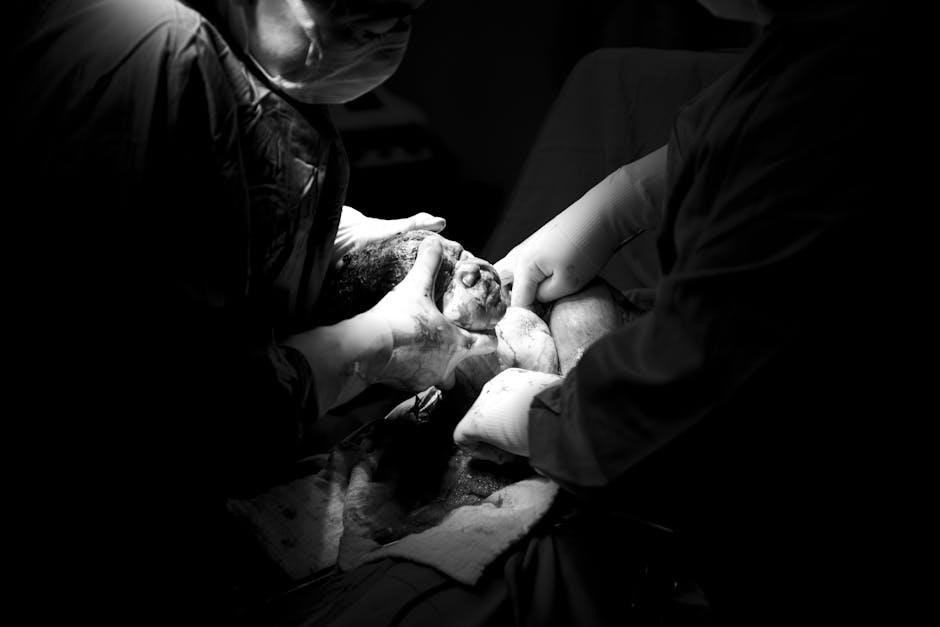
Neonatal ventilator settings require careful consideration of patient needs and medical guidelines to ensure proper respiratory support and care for newborns every day.
Importance of Ventilator Settings in Neonatal Care
Proper ventilator settings are crucial in neonatal care as they directly impact the health and well-being of newborns. According to medical guidelines, ventilator settings must be carefully considered to ensure that the patient receives the right amount of oxygen and respiratory support. The importance of ventilator settings cannot be overstated, as improper settings can lead to serious health complications. A clear understanding of ventilator settings is essential for healthcare professionals to provide optimal care for newborns. By following established medical guidelines and best practices, healthcare professionals can ensure that ventilator settings are tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient, resulting in better health outcomes and improved quality of life for newborns. Effective ventilator settings require a comprehensive approach to neonatal care, taking into account the patient’s medical history, current condition, and ongoing needs.

Understanding Neonatal Respiratory Distress
Neonatal respiratory distress requires immediate medical attention and proper care to ensure the newborn’s health and safety always matters.
Causes and Symptoms of Respiratory Distress in Neonates
Respiratory distress in neonates can be caused by various factors, including premature birth, infection, and congenital heart disease, which can lead to symptoms such as rapid breathing and chest retractions. The diagnosis of respiratory distress is typically made through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as chest X-rays and blood gas analysis. According to the Michigan Society for Respiratory Care, early recognition and treatment of respiratory distress are crucial to prevent long-term complications and improve outcomes for neonates. A thorough understanding of the causes and symptoms of respiratory distress is essential for healthcare providers to provide effective care and support for neonates with respiratory distress. This knowledge can help guide the development of effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. Neonatal care requires attention to detail.
Types of Ventilation for Neonates
Neonates receive various ventilation types, including non-invasive and invasive methods, daily.
High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation and Its Applications
High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV) is a type of ventilation used in neonatal care, particularly for patients with severe respiratory distress. This method involves the use of a high-frequency oscillator to deliver small tidal volumes at a rapid rate, typically between 3-15 Hz. The applications of HFOV are varied, including the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and pulmonary interstitial emphysema. HFOV has been shown to be effective in improving oxygenation and reducing lung injury in neonates. The use of HFOV requires careful consideration of patient needs and medical guidelines to ensure proper respiratory support and care. Additionally, HFOV can be used in conjunction with other ventilation methods to provide optimal care for newborns with respiratory distress. Overall, HFOV is an important tool in the management of neonatal respiratory care.

Guidelines for Neonatal Ventilator Settings
Neonatal ventilator settings guidelines are established by medical professionals to ensure proper care and support for newborns with respiratory issues every day always.
Recommended Settings for Different Neonatal Conditions
Neonatal ventilator settings vary depending on the condition of the newborn, with different settings recommended for conditions such as respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, and congenital heart disease. The American Academy of Pediatrics provides guidelines for neonatal ventilator settings, including recommendations for tidal volume, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. Additionally, the National Institutes of Health provides information on the use of ventilators in neonatal care, including recommendations for different neonatal conditions. The goal of these guidelines is to provide optimal care and support for newborns with respiratory issues, and to improve outcomes for these patients. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure that newborns receive the best possible care and support. Neonatal ventilator settings are a critical aspect of neonatal care, and require careful consideration of patient needs and medical guidelines.
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
Weaning process involves gradual reduction of ventilatory support to facilitate independent breathing in neonates slowly every day.
Gradual Process of Withdrawal from Ventilatory Support
The gradual process of withdrawal from ventilatory support is a critical step in the care of neonates, requiring careful planning and monitoring by medical professionals. This process involves a series of gradual reductions in ventilatory support, allowing the neonate to adapt to independent breathing. According to the Michigan Society for Respiratory Care, a not-for-profit professional association, this process should be guided by established medical guidelines and protocols. The Child and Adolescent Health Service also provides resources and support for families and healthcare professionals involved in the care of neonates. By following a gradual and well-planned approach to withdrawal from ventilatory support, healthcare professionals can help ensure a safe and successful transition for neonates. This approach is essential for promoting the best possible outcomes for these vulnerable patients.

Home Care for Neonates on Ventilatory Support
Home care for neonates on ventilatory support involves parental administration of medication and close monitoring of patient needs daily.
Parental Administration of Intravenous Medication and Home Visits
Parental administration of intravenous medication is a crucial aspect of home care for neonates on ventilatory support, requiring careful training and supervision by medical professionals. The process involves teaching parents how to administer medication safely and effectively, as well as monitoring the patient’s condition and responding to any changes or complications that may arise. Home visits by medical staff are also an essential component of this care, providing an opportunity for regular check-ups and assessments of the patient’s progress. By working together, parents and medical professionals can ensure that neonates receive the best possible care and support in the comfort of their own homes, with the use of guidelines and resources to facilitate this process and improve patient outcomes. Regular communication and collaboration are key to successful home care.
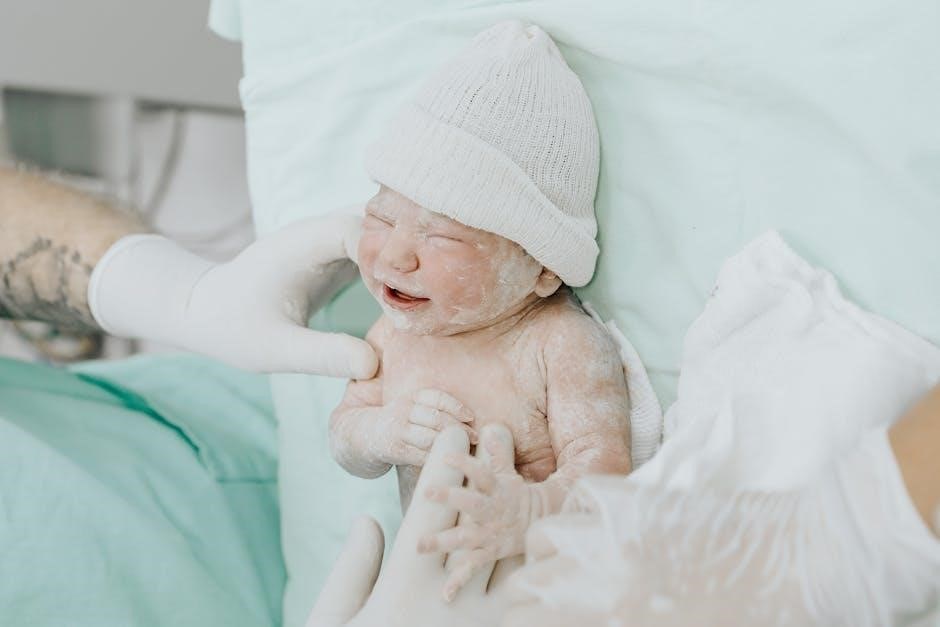
Professional Associations and Resources
Michigan Society for Respiratory Care and Child and Adolescent Health Service provide resources and support for neonatal care professionals every day.
Michigan Society for Respiratory Care and Child and Adolescent Health Service
The Michigan Society for Respiratory Care is a professional association that provides education and resources for respiratory care professionals, including those working in neonatal care. The Child and Adolescent Health Service is a healthcare organization that provides medical care to children and adolescents, including neonates. Both organizations are committed to promoting health and well-being in their respective communities. They offer a range of services, including education, advocacy, and clinical care. Their websites provide access to a wealth of information, including guidelines, protocols, and best practices for neonatal care, as well as information on upcoming events and conferences. These organizations play a critical role in supporting the health and well-being of neonates and their families, and are valuable resources for healthcare professionals working in this field, with many online resources available.